Lesson01 08/24/2022
- words
- reflective
- refractive 折射的
- pan 移動拍攝
- cone 圓錐
- Blender operations
- Typical workflow: select an object, modify its properties
- Changing view:
- Arbitrary change: press middle mouse button and drag, or you can drag the xyz coordinates on the top right corner
- Pan view(horizontal / vertical movement only): press shift key and press middle mouse button and drag
- Zoom in/out: scroll up/down with middle mouse button
- You can also use the view panel to change view direction
- Deleting an object: select the object and press key x
- Adding a new object: use the add menu to add a new object, or you
can use
SHIFT+Ato add a new object - Transforming objects
- Scale: select the object, press
S, then drag to scale the object, left click to confirm/right click to cancel, useS+X/Y/Zto scale along the x/y/z axis. You can useS(+X/Y/Z) +a numberto scale the object to a specific size - Rotate: select the object, press
R, then drag to rotate the object, left click to confirm/right click to cancel, useR+X/Y/Zto rotate the object along the x/y/z axis - Translate(move): select the object, press
G, then drag to move the object, left click to confirm/right click to cancel, useG+X/Y/Zto move along the x/y/z axis
- Scale: select the object, press
- Duplicate objects: select the object, then
SHIFT+Dto duplicate the object, you can duplicate multiple objects by selecting multiple objects and thenSHIFT+D - Set the parent of an object
- If object A is the parent of object B, then object B will move along with object A
- How: select object B, then select object A, then press
CTRL+Pto set object A as the parent of object B - If there are multiple objects selected, then the last selected object will be the parent of the other selected objects
Lesson02 08/29/2022
- Blender operations
- Change the origin of an object: select the object, choose
set originin theobjectmenu, thenorigin to 3D cursor
- Change the origin of an object: select the object, choose
- Simple mesh objects...
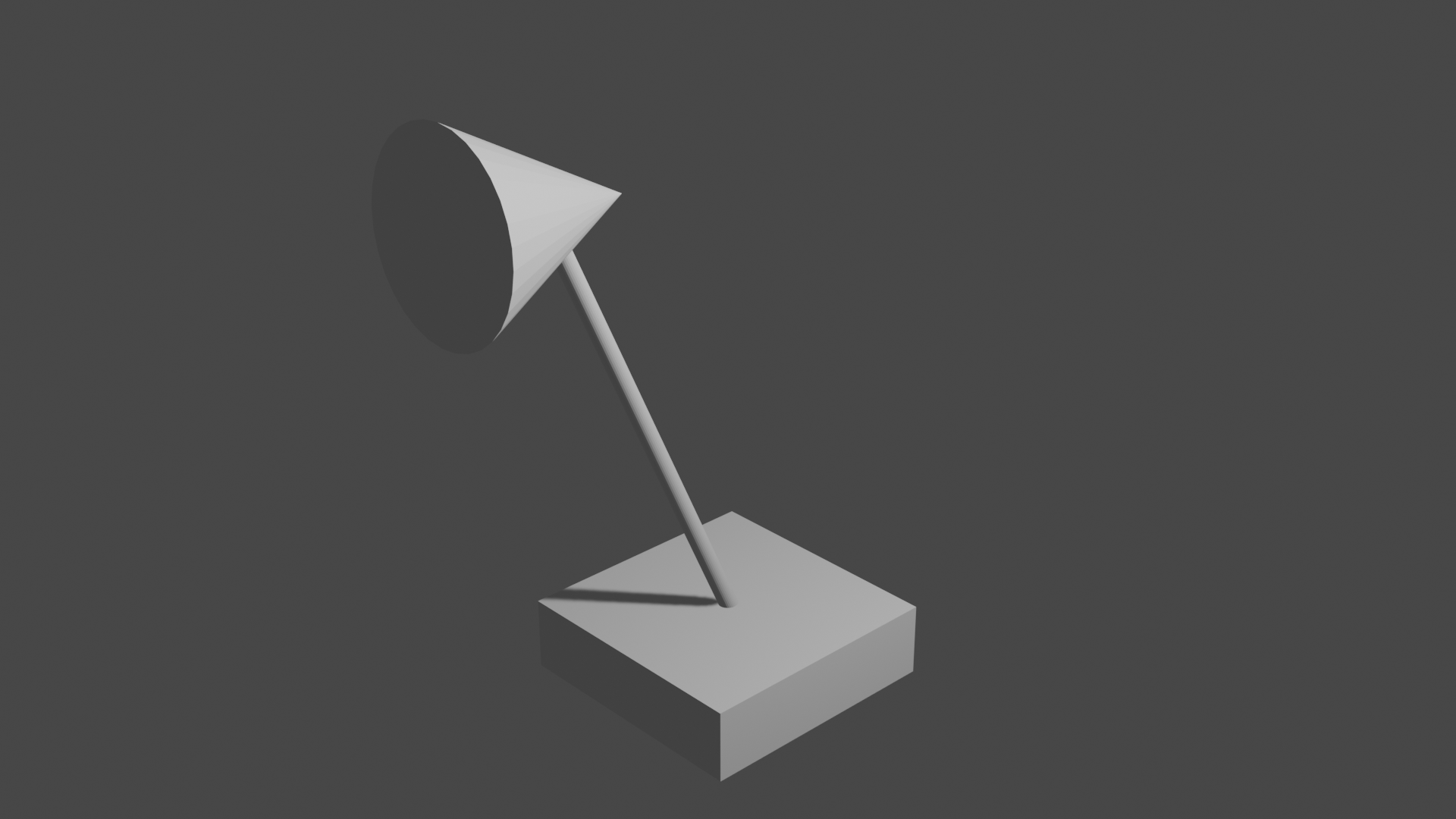
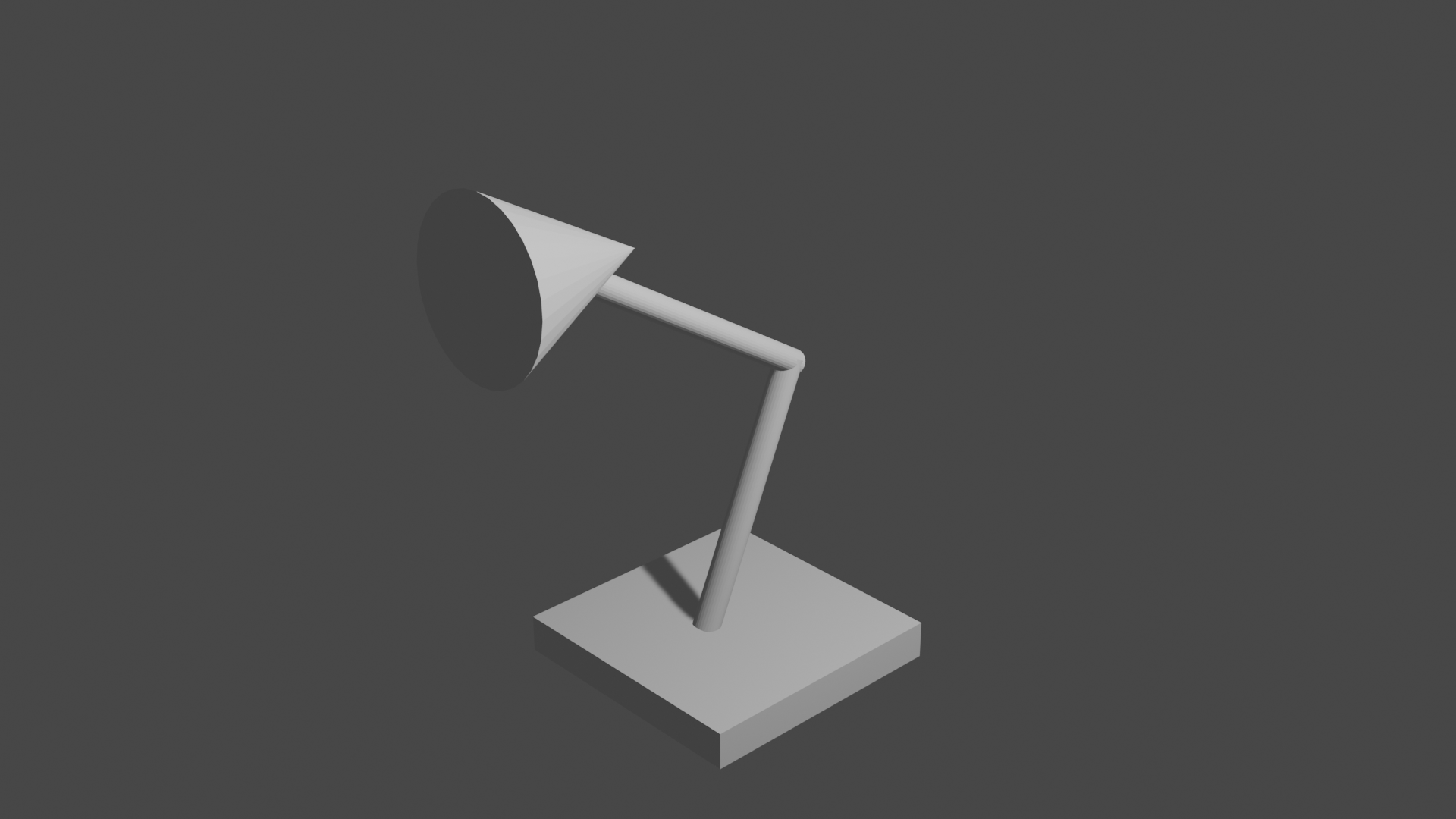


Lesson03 08/31/2022
Materials
- Principled BSDF(bidirectional scattering distribution function): the most commonly used material
- BSDF is a superset and the generalization of the BRDF(bidirectional reflectance distribution function) and BTDF(bidirectional transmittance透光度 distribution function)
- Change the viewpoint shading options to view the materials:
wireframe綫框,solid(materials invisible),material preview(use Eevee as renderer),rendered(can use other renderers) - Change the shading of an object: select the object, click the
objectmenu, chooseShade Smooth(default isShade Flat) - Make the surface reflective:
metallic = 1,roughness = 0, change the render engine toCycles - If you use the
Cyclesrenderer, you let the renderer use fewer samples, so your computer will not stuck and the whole process will be faster
Mesh editing
- Use
Tabto change betweenObject modeandEdit mode - In edit mode, you can select vertices, edges, and faces
- You can create a material and assign it to part of an existing
object
- Use
Simple material objects
The plane below is totally reflective
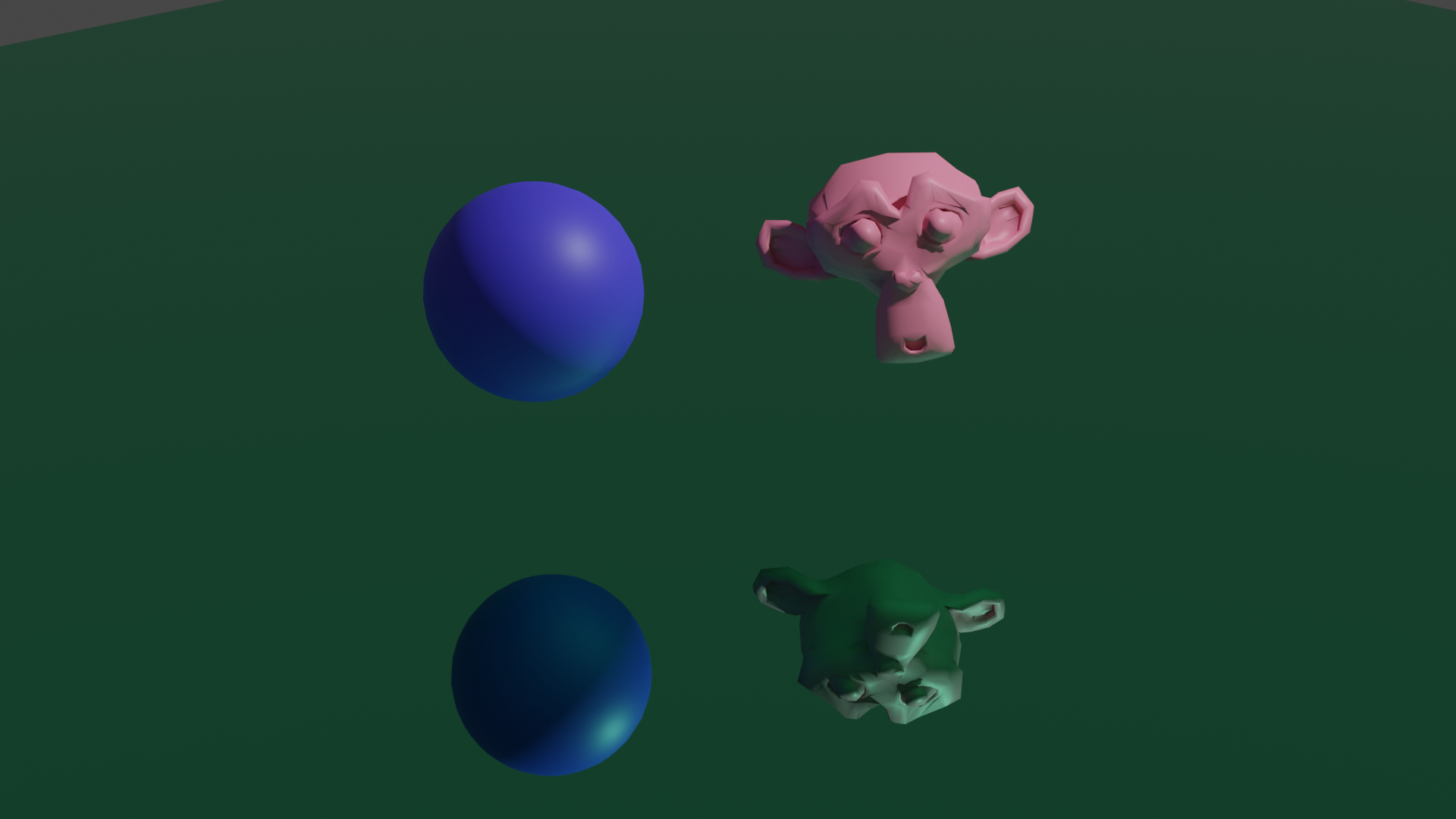

Lesson04 09/01/2022
Subdividing a plane
- Change from object mode to edit mode, select the whole plane, and
choose
Subdividein theEdgemenu - You can number of cuts inside one subdivision
- Change from object mode to edit mode, select the whole plane, and
choose
Proportional Editing
- If you want to edition to a vertex influence its neighbors, you can use proportional editing
- All vertices inside the target circle area will be affected, you can use the middle button to change the size of the circle
- When you are done with proportional editing, you should turn it off to avoid accidentally editing other vertices
Extrusion modeling
- Extrude Faces duplicate faces, while keeping the new geometry connected with the original vertices
- Change from object mode to edit mode, select the face you want to
extrude, use shortcut
Eto extrude, or use theExtrude facesin theFacemenu
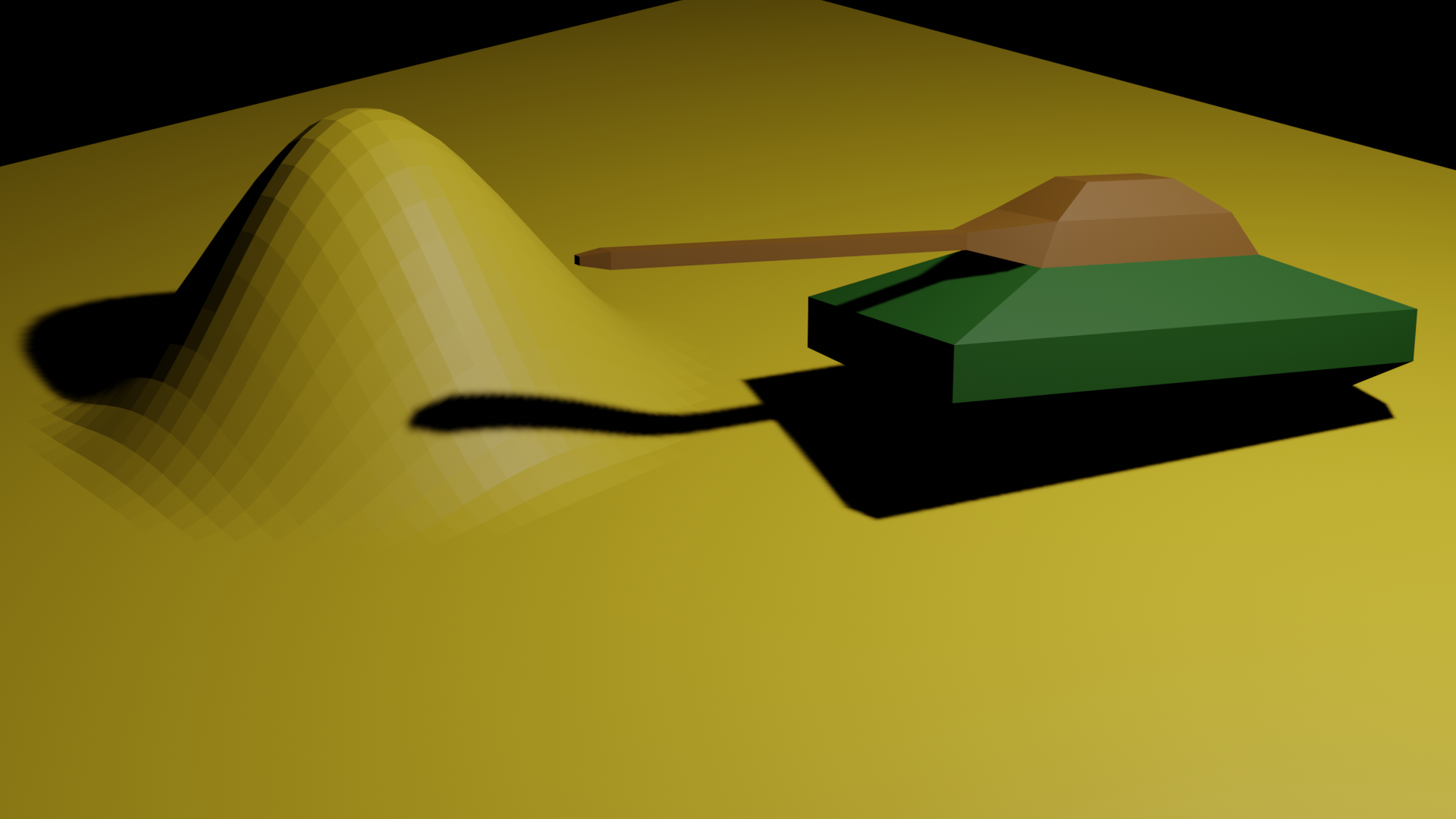
Modifiers
- Modifiers are automatic operations that affect an object’s geometry in a non-destructive way
- With modifiers, you can perform many effects automatically that
would otherwise be too tedious to do manually and without affecting the
base geometry of your object
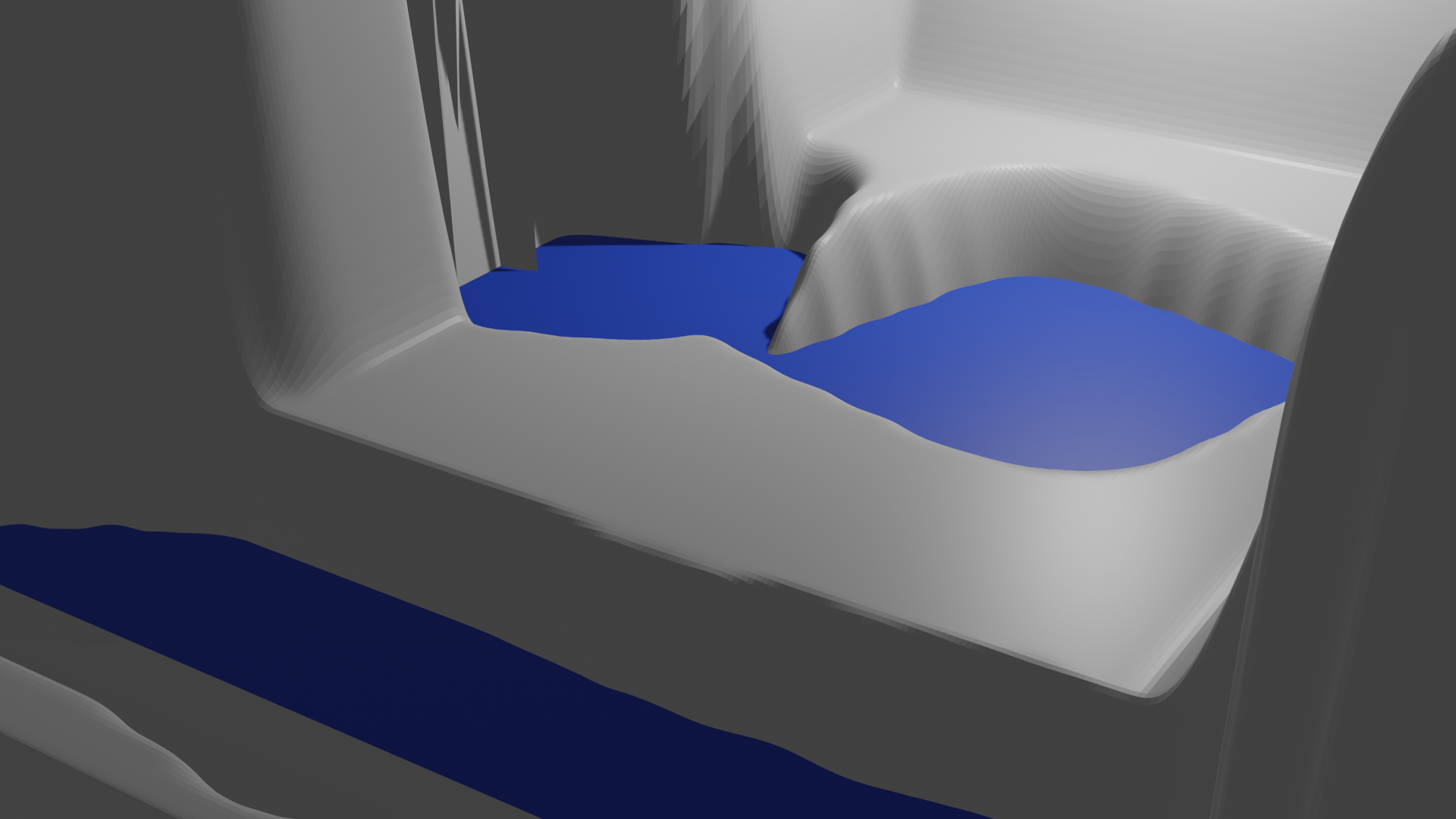
Simple objects
This is a picture of my room, it contains a L-shaped desk with a computer on it, an office chari, a floor lamp, a book shelf and a bed
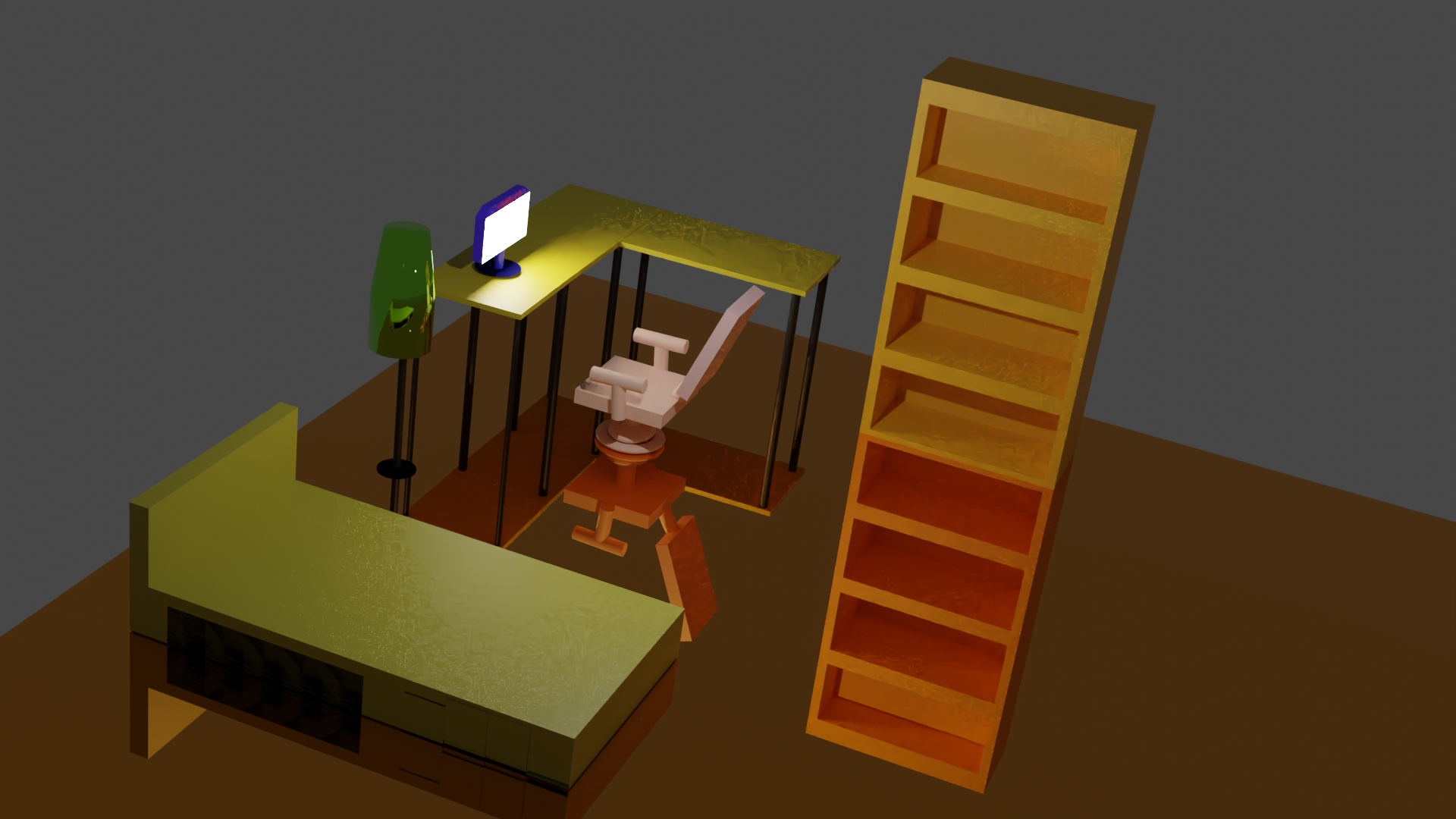

Lesson05 09/07/2022
- Textures (纹理) Intro
- There are two types of textures: environment textures and object textures
- You can use online texture websites to find textures
- Environment textures
- Change from
layouttoshadingin the top menu - Select the
Worldoption in the shader type menu - Choose a source file for the environment texture, and link its
colorproperty to thesurfaceproperty of theWorld Output - You need to change the
Viewpoint ShadingtoRenderedto see the environment texture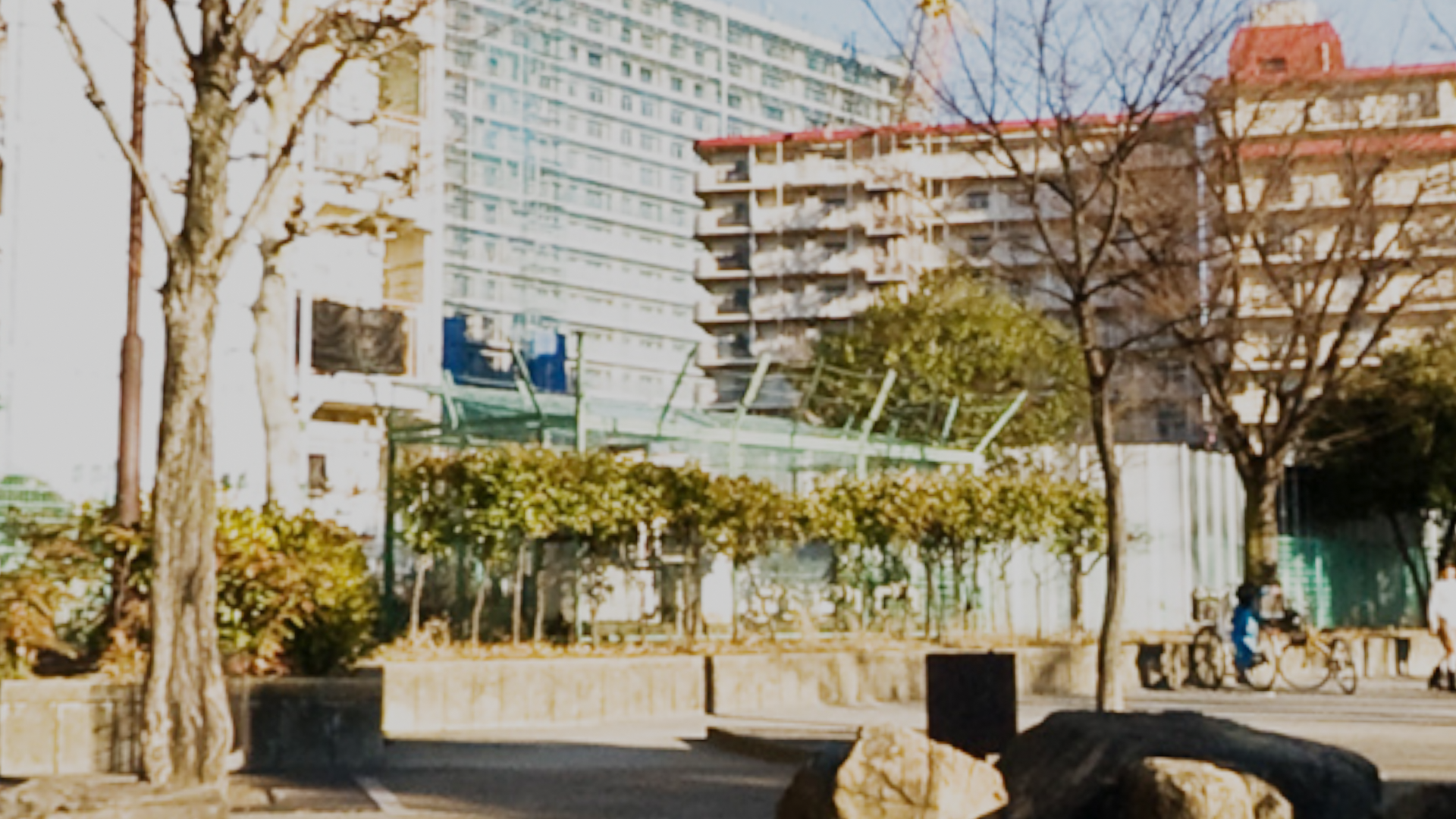
- Change from
- Object texture
- Change from
layouttoshadingin the top menu - Select the
Objectoption in the shader type menu - Use the
Addbutton, chooseShader, then choosePrincipled BSDF - Drag a source texture file into the shading view, link its
Colorproperty to theBase Colorproperty of thePrincipled BSDF - Link the
BSDFproperty of thePrincipled BSDFto theSurfaceproperty of theMaterial Output - You need to change the
Viewpoint ShadingtoRenderedto see the object texture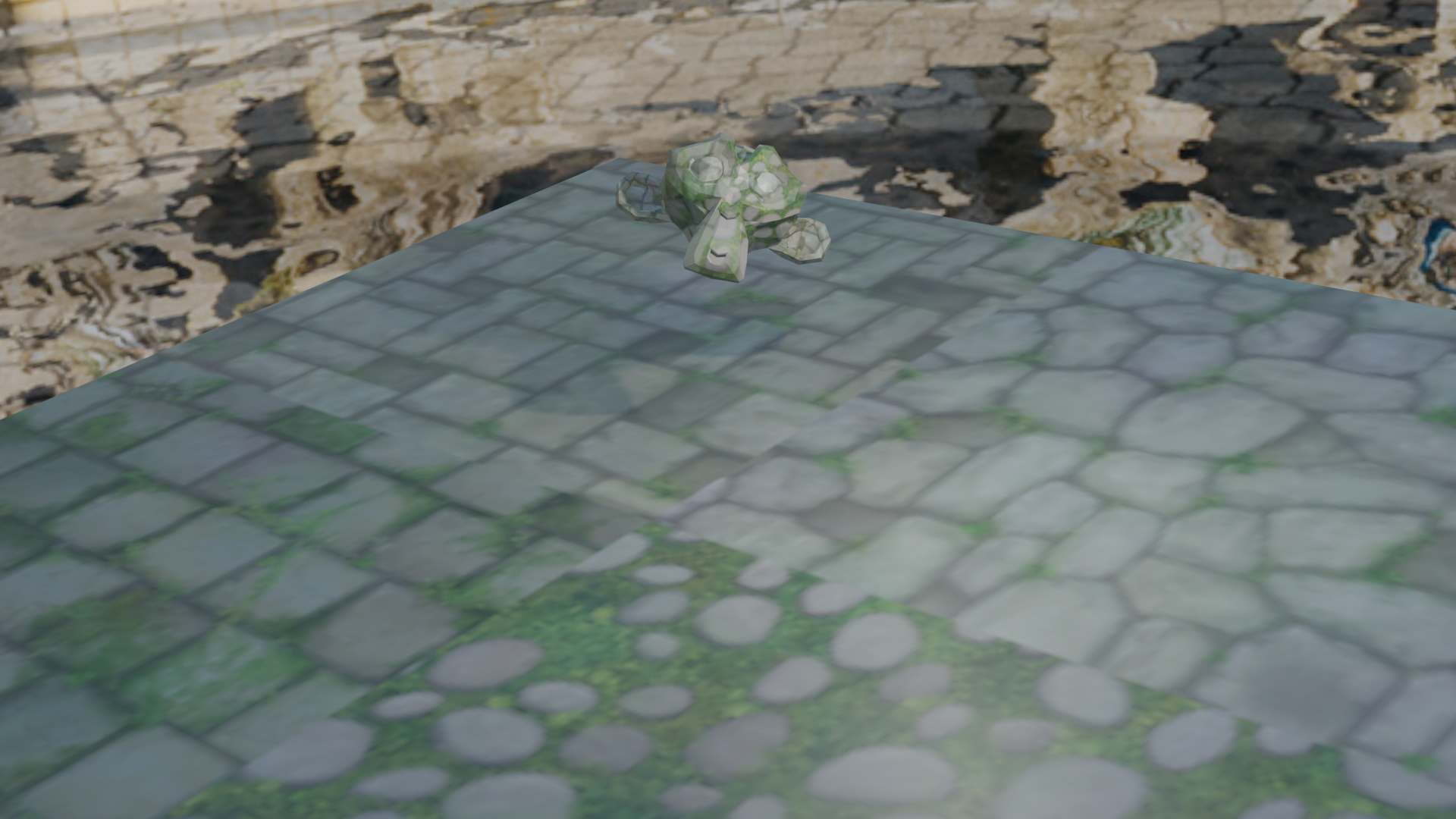
- Change from
Lesson06 09/08/2022
- Material nodes
- You can choose different shaders to create different surfaces
- You can combine different shaders on the same object: create
multiple shaders, then use them as inputs of the
Mix Shadernode, and then link theMix Shadernode to theMaterial Outputnode. You can also choose the weight of each input shader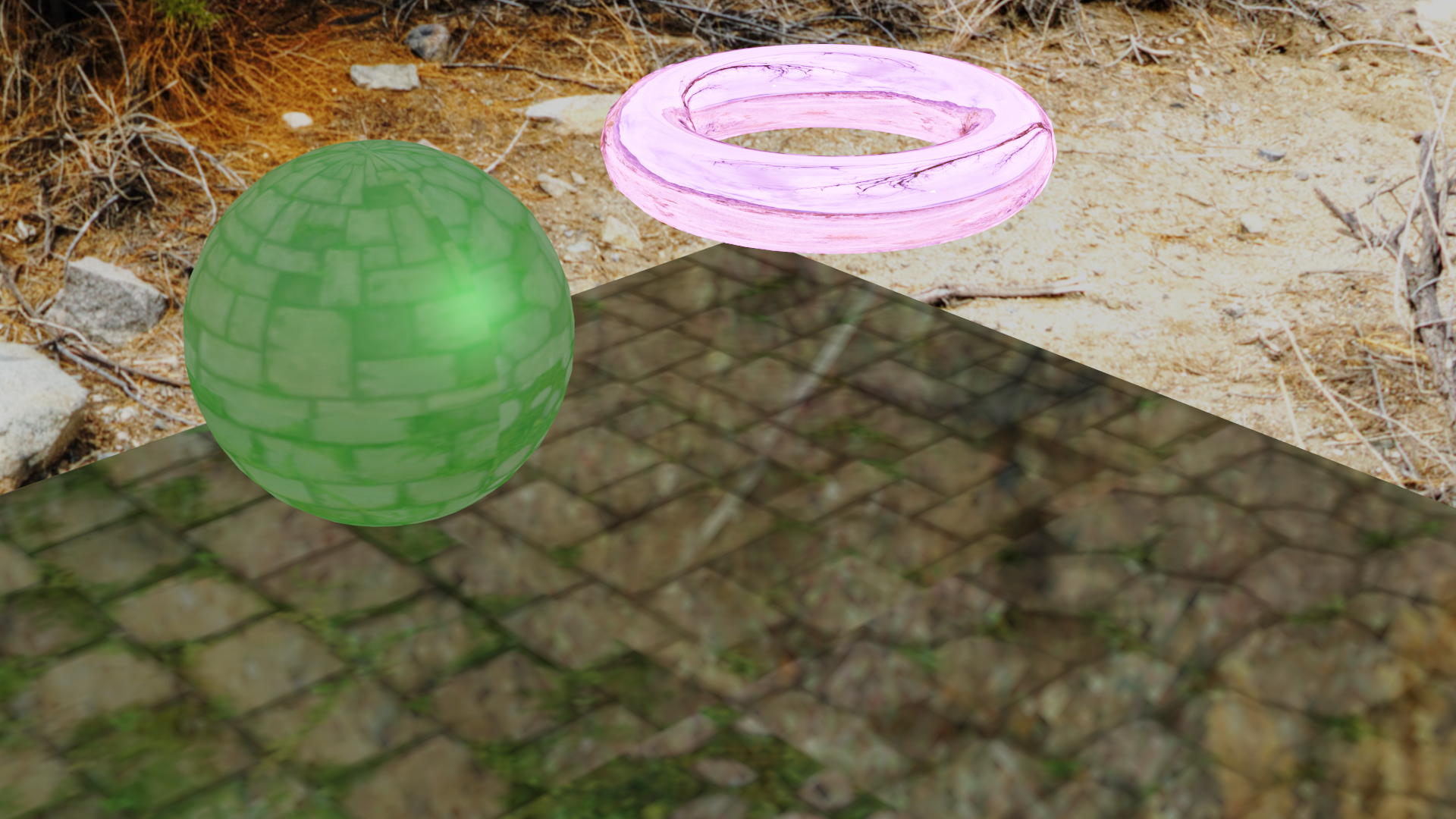
- UV Mapping
- Click the
UV Editingbutton in the top menu - The surface of a 3D object is mapped to a 2D figure on the UV plane
- You can move, resize, rotate the figure on the UV plane as you do in
the normal layout view
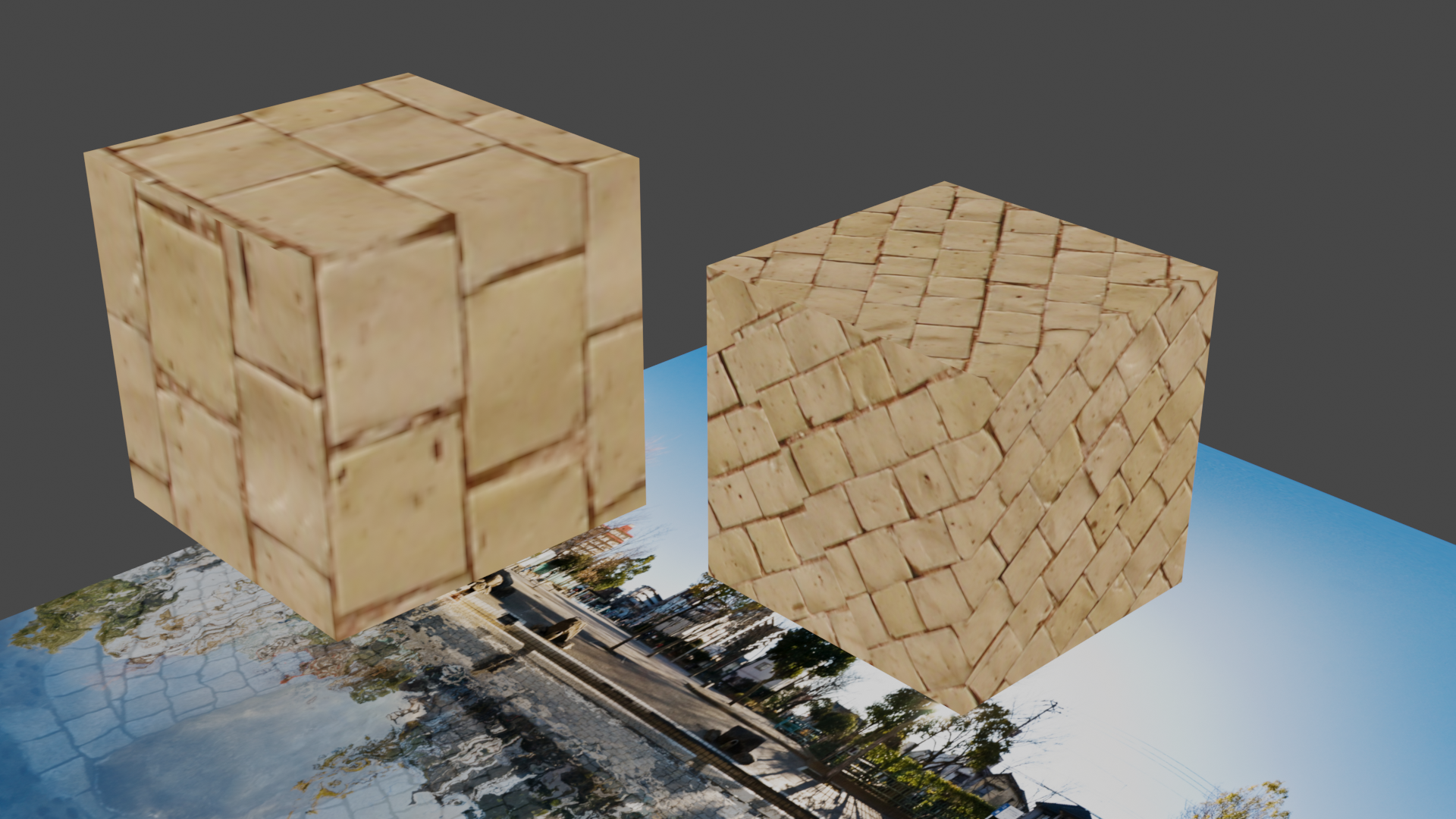
- Click the
Lesson07 09/12/2022
- Text
- Create text and then convert it to
mesh(
object->convert->mesh), then you can add materials to it - Then you add modifiers:
add modifier->solidify-> changethickness
- Create text and then convert it to
mesh(
- Light
- You can add different types of lights: point light, sun light, area light, spot light
- You can change the color, power of your light
Lesson08 09/14/2022
- Use normal map(法线贴图) to create objects with uneven
surface(imitate roughness)
- Create two
Image Texture - Connect one
Image Textureto theBase ColorofPrincipled BSDF, connect the other to theNormalofPrincipled BSDF - Connect the
BSDFof thePrincipled BSDFto theSurfaceof theMaterial Output
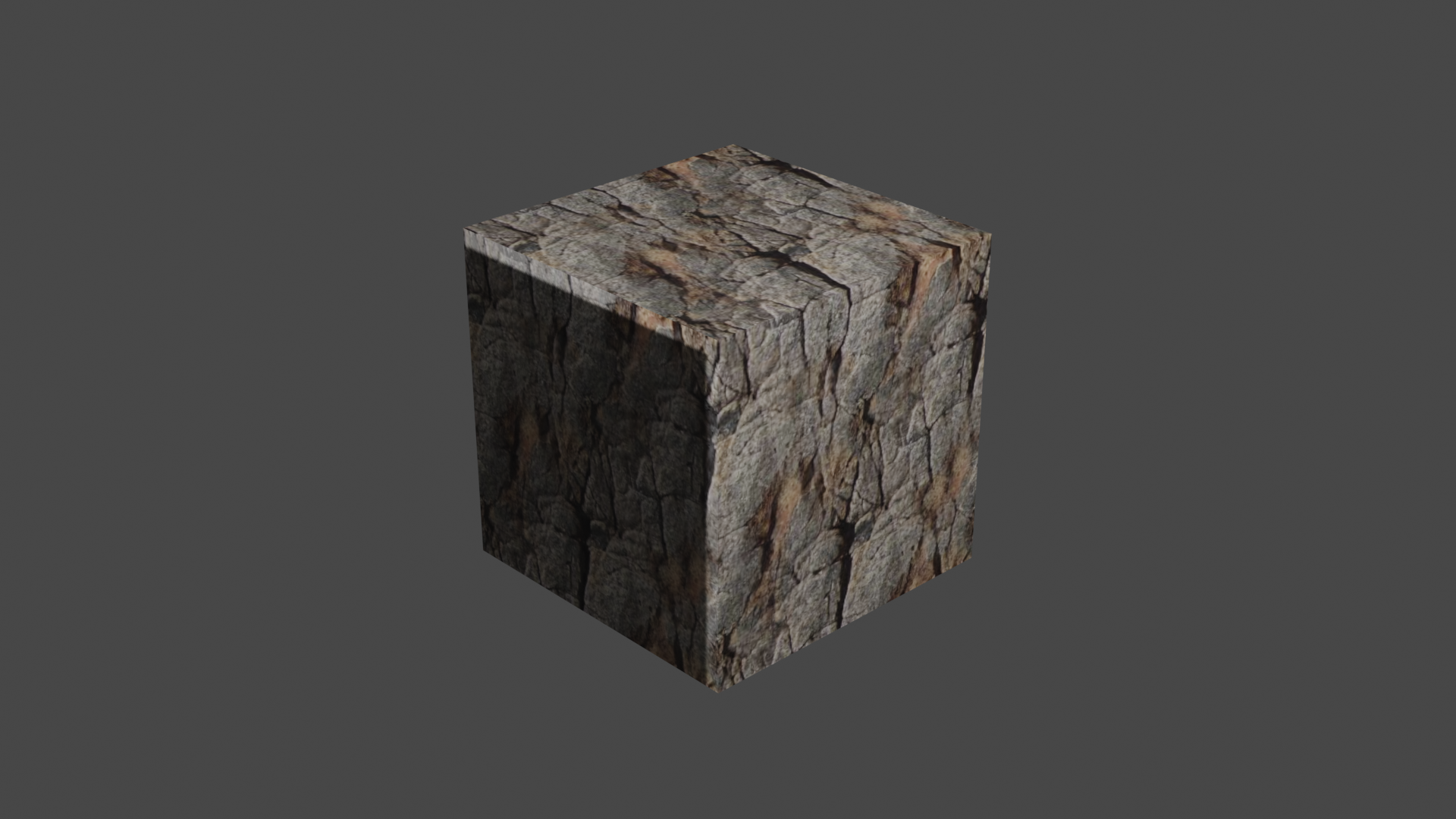

- Create two
Lesson09 09/15/2022
- Practice for the coming quiz
Lesson10 09/19/2022
- Use Texture paint mode to paint textures on an object
Lesson11 09/20/2022
Transformation of point
- Translation:
- Scaling:
- Rotation: let
- Translation:
Transformation can be composed
Lesson12 09/22/2022
- Animation
- Default 25 frames/second
- Use
ito insert a keyframe, you can change location, rotation, scale and other custom properties of the object - Modify
Output Propertiesto change the output format toAVI JPEG, then render animation, there will be anavifile in the output folder
Lesson 13 09/29/2022
- Exam 1 on modeling: got 100/100
Lesson 14 09/29/2022
Lesson 15 10/03/2022
- 3D printing
Lesson 16 10/06/2022
Jump lamp example
Use armature to add bones to the model
- Select
Layoutmodel, then selectAdd->Armature
- Select
Lesson 17 10/12/2022
- Add armature
- Use
Ctrl + Alt + Qto change to a quad view and back - Make sure that the armature is inside the object when you setting
the parent(so some neighbor points are assigned to the armature), the
armature should be the parent of the object, and use the
With Automatic Weightsmode to automatically assign points - Use the
Pose Modeof the armature to change the position of the bones as well as the object - If you cannot see the armature, Click the
Object Data Propertieson the right, in theViewport Displaysection, check theIn Frontoption in theShowsection - Select the armature and the object to which is the child, then
select the
Weight Paintmode, then you can adjust the influence of the armature on the object - You can change the end frame when rendering animation
- Use
Lesson 18 10/13/2022
- Makeup exam: did not take it because I got 100/100 on the first exam
Lesson 19 10/18/2022
You can use some online free
fbxhuman model and import it into blender, which contains both model object and its armatureRigify
- Click the top left button, select
Preferences, in theadd-onssection, searchrigify, check theRigging: Rigifyoption - For human model, select
Add->Armature, then selectHuman(Meta-rig) - Use the Pose Mode of the armature to adjust its position
- Click the top left button, select
Lesson 20 10/19/2022
- Shape Key animation
- Create an object model, click
Object Data Propertieson the right, Click+in theShape Keyssection to add a basic shape key - Add other shape keys, go to
Edit Mode, click the shape key you want to edit, do some modifications on the model, then go back toObject Mode, adjust thevalueto show the influence of that shape key - For animation, select a key frame, pause your mouse on the value of
each shape key, press
ion the keyboard, then move to the next key frame
- Create an object model, click
Lesson 21 10/20/2022
- Practice exam 2
Lesson 22 10/24/2022
Lesson 23 10/25/2022
Lesson 24 10/27/2022
- Practice exam 2 (this should be exam 2, but there was an network error in the classroom)
Lesson 25 10/31/2022
- Exam 2 on animation: got 100/100
Lesson 26 11/02/2022
- Class cancelled...
Lesson 27 11/03/2022
- Reviewing CPA 2