Week 1
01/18/2022
Analysis of Fibonacci
The runtime is exponential. Actually you can calculate the formula:1
2
3
4
5
6function fib(n)
if n = 0 then
return 0
if n = 1 then
return 1
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2)The runtime is linear1
2
3
4
5
6
7function fib(n)
create an array of size n called fibArray
fibArray[0] = 0
fibArray[1] = 1
for i = 2 to n
fibArray[i] = fibArray[i-1] + fibArray[i-2]
return fibArray[n]Analysis of arithmetic
- Addition: x, y are n bit integers, adding them together is an
- Subtraction: x, y are n bit integers, subtracting them together is
an
- Multiplication: x, y are n bit integers, multiplying them together
is an
- The russian peasant algorithm
- Halve on the first column, double on the second column, repeat this until the item in the first column is 0
- Remove all rows that have an even item in the first column
- Add up the remaining items in the second column This algorithm is a
a
- Addition: x, y are n bit integers, adding them together is an
01/20/2022
- Analysis of multiplication using divide and conquer
Problem: x, and y are n bit integers, calculate the multiplication of them using divide and conquer
Divide x and y into two halves:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8MULT(x, y)
a1, a2 <- a
b1, b2 <- b
p1 <- MULT(a1, b1)
p2 <- MULT(a1, b2)
p3 <- MULT(a2, b1)
p4 <- MULT(a2, b2)
return 2^n * p1 + 2^{n/2} * (p2 + p3) + p4This algorithm is a
Rule of thumb: sum of an increasing geometric series is
1
2
3
4
5
6
7MULT(x, y)
a1, a2 <- a
b1, b2 <- b
p1 <- MULT(a1, b1)
p2 <- MULT(a2, b2)
p3 <- MULT(a1 + a2, b1 + b2)
return 2^n * p1 + 2^{n/2} * (p3 - p1 - p2) + p2This algorithm is a
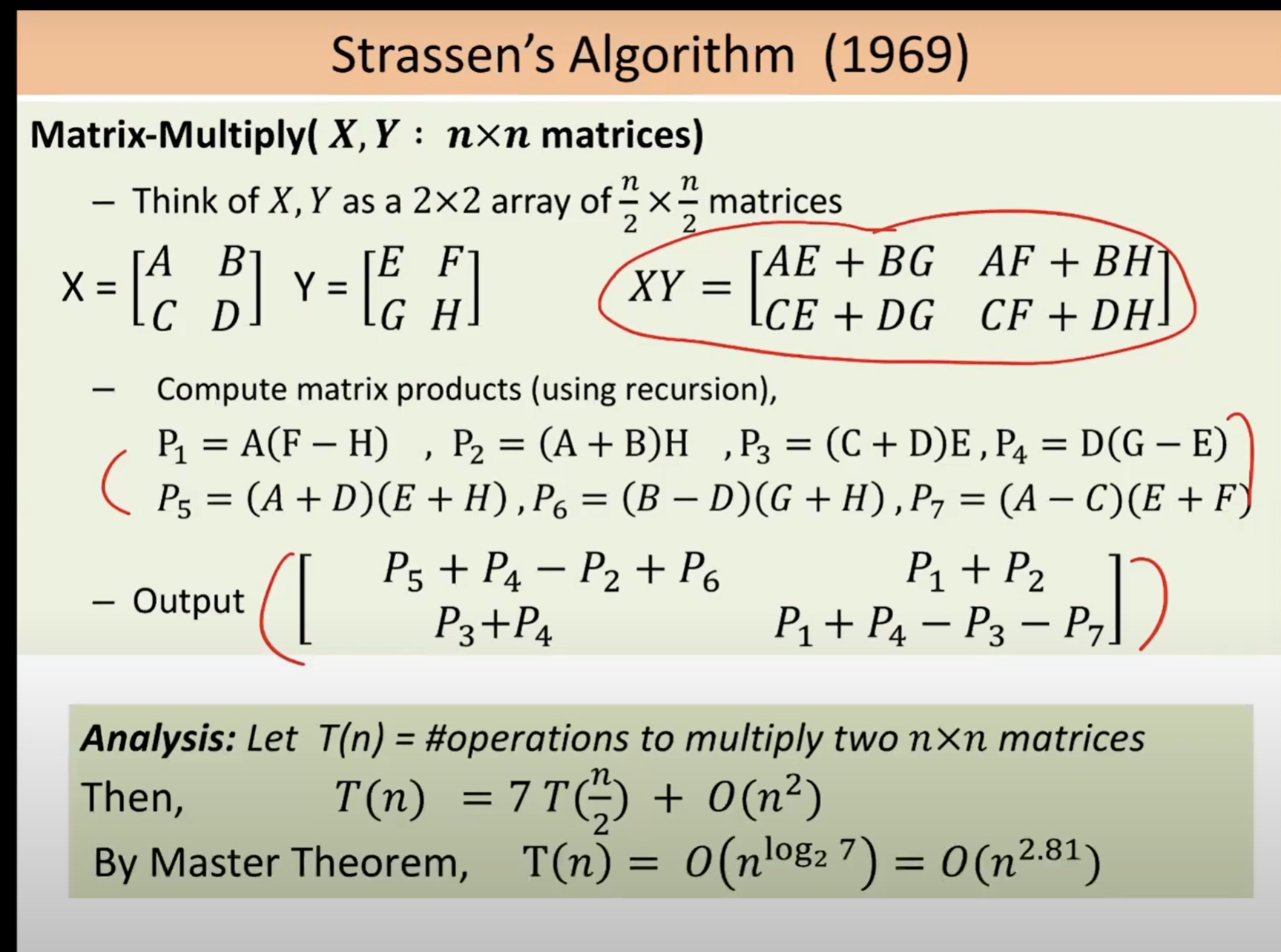
- Analysis of matrix multiplication using divide and conquer
- Problem: given two n * n matrices A, and B, calculate A * B
- The naive algorithm:
- Use divide and conquer
- Divide the n * n matrix into four n/2 * n/2 matrices
- The recurrence relationship is :
- Improvement